It’s clear that the listening habits of headphone enthusiasts are changing. Recently, HiFiMan launched the Ananda BT headphones -- a Bluetooth version of its Ananda planar-magnetic headphones -- which, at $1199 USD, are arguably the first true audiophile-grade Bluetooth headphones. Clearly, there must be some interest even among hardcore headphone enthusiasts for playing music -- or whatever -- from smartphones.
That “whatever” represents another big change. No longer can we assume that most of the material heard through headphones will be music -- or at least only music. While most audiophiles still listen mostly to music unaccompanied by other media, younger audio enthusiasts are likely to use their headphones, at least part of the time, to listen to the soundtracks of music videos, TV shows, movies, and video games they watch on their smartphones and tablets.
 Three products equipped with aptX Low Latency -- the MEE Audio Matrix Cinema ANC headphones, the KLH Ultimate Two earphones, and the MEE Audio Connect transmitter
Three products equipped with aptX Low Latency -- the MEE Audio Matrix Cinema ANC headphones, the KLH Ultimate Two earphones, and the MEE Audio Connect transmitter
The challenge when combining video and audio content is making sure the audio synchronizes with the video. If it doesn’t, you’ll get lip-sync problems, and all your video programming will start to remind you of badly dubbed Japanese monster movies of the 1960s. Lip-sync problems tend to happen with Bluetooth -- not because the transmission adds delay (it travels at the speed of light), but because of the delay, or latency, caused by having to encode and decode the audio in the format used for transmission.
When Bluetooth was used only for phone conversations and music playback, the 200- to 250-millisecond typical latency of the format’s standard SBC codec didn’t matter much. But with video playback and gaming becoming more common uses of headphones, 200ms is no longer acceptable for many Bluetooth headphone buyers. This performance fails to meet the maximum 45ms audio latency standard of the US Advanced Television Systems Committee or the looser 125ms standard of the International Telecommunication Union.
Fortunately, new technologies have come along that are intended to improve on SBC’s lousy latency numbers. The aptX codec, now owned by Qualcomm, has inherently lower latency than SBC, but the aptX Low Latency codec -- launched in 2013 but only now starting to find widespread use -- promises 32ms latency, which meets even the tough ATSC standard. That means the audio will lag the video by just a single frame, assuming the common 30fps video frame rate.
Now that a few Bluetooth transmitters with aptX Low Latency have become available, I’ve had a chance to find out whether the technology works as well as Qualcomm claims. In the following measurements, I’ll show you the difference between using a standard SBC Bluetooth transmission (from a Sony HWS-BTA2W transmitter) and standard aptX and aptX Low Latency transmissions (from a MEE Audio Connect transmitter). Neither of these transmitters had a significant effect on the frequency response of the headphones I tested -- but the differences in latency were huge.
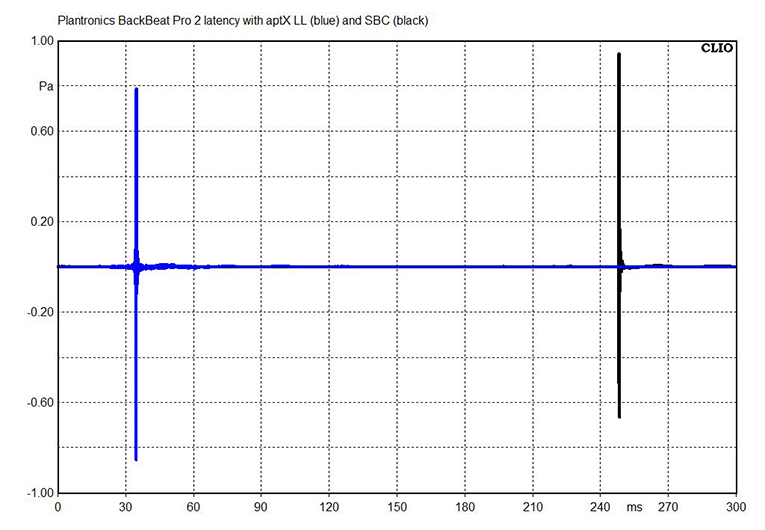
In the above chart, we see the impulse response of the Plantronics BackBeat Pro 2 headphones when they’re fed a standard SBC signal and when they’re fed an aptX Low Latency signal. The difference is stark: 34ms for aptX Low Latency and 248ms for SBC. In other words, imperceptible latency versus latency that’s impossible to ignore. With MEE Audio’s own Matrix Cinema ANC headphones, the results were slightly (although imperceptibly) better: 31ms for aptX Low Latency.
I also ran this test with the Sennheiser Momentum True Wireless earphones, which include aptX Low Latency. These didn’t do quite as well, although their latency was still relatively low: 54ms. I assume this extra latency is due to the true wireless design, in which the audio has to be delayed slightly so the earphones can be synchronized.
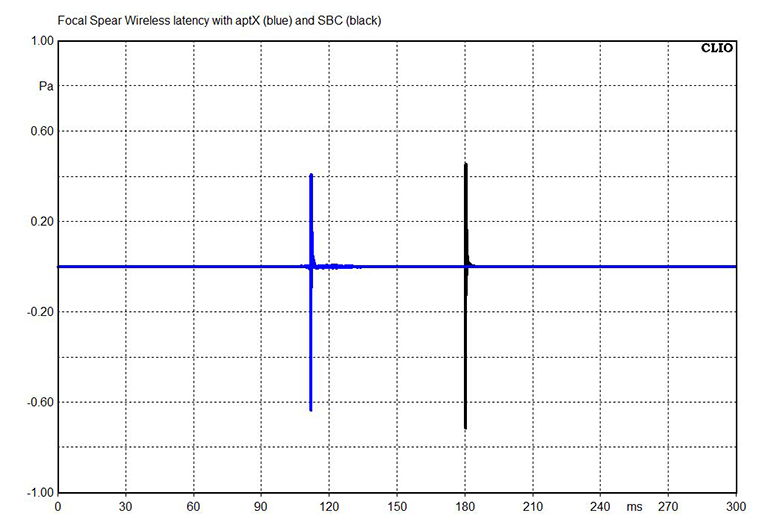
This chart shows the latency of Focal’s Sphear Wireless Bluetooth earphones, which are equipped with standard (not Low Latency) aptX, when they’re fed with SBC and standard aptX signals. The difference here isn’t as dramatic: 112ms for aptX versus 181ms for SBC. Still, it shows that even standard aptX achieves significantly lower latency than SBC.
What does that mean for you, though? It’s hard to mentally translate latency measured in video frames or milliseconds into real-world effects, so I created a video to show you what latency of 0ms, 33ms, 100ms, 200ms, and 300ms look and sound like.
The good news is, aptX Low Latency effectively eliminates any concerns about latency when you’re watching videos or playing video games. While the sonic benefits of different audio codecs can be hard to hear, this is a difference that’s easy to appreciate and -- for anyone who uses headphones for YouTube and/or video games -- well worth paying for.
. . . Brent Butterworth







